| |
USB Power Delivery Will Unify the Charging Standards
for Household Electronics and Mobile Devices
Wilson Hou, Staff Design Engineer of Avnet Design Services, Asia Pacific

Quick Charge is the Future Trend of Mobile Phone Development
Mobile phone hardware has undergone rapid developments in recent years, in which CPUs have evolved from low-clock speed, single-core CPUs to high-clock speed, multi-core CPUs (e.g., high-clock speed quad-core, octa-core, and ten-core CPUs). However, as these hardware features improved, battery life-related bottlenecks ensued. In contrast to to the rapid developments of mobile phone hardware, battery technologies have stalled for years as effective methods for enhancing battery density remain yet to be found. At present, battery density increases have been made using the primitive method of increasing battery capacity (e.g., from 3000 mAh to 4000 mAh, and from 4000 mAh to 5000 mAh). Although increased battery capacity can increase battery life, it creates the problem of long charging time; because traditional mobile phone chargers have relatively low charging efficiencies, large-capacity phone batteries require long charging times. Thus, when mobile phones run out of power, a considerable amount of time is required to fully recharge the battery. In response to this problem, companies have proposed a solution: quick charge technology. This technology enables chargers to provide, in less than twenty minutes, the same amount of power that traditional chargers require an hour to provide, which significantly enhances charging speeds and reduces charging times.
 (Image source / Qualcomm) (Image source / Qualcomm)
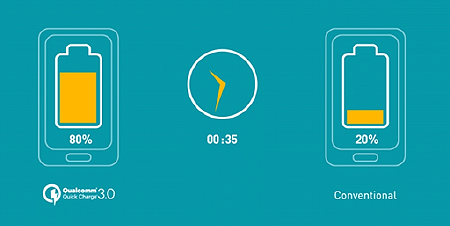
The left side of the image shows quick charge technology, whereas the right side of the image shows a traditional charging technology. The result shows that after 35 minutes of charging, the traditional charging method provided only 20% of power to the mobile phone, whereas the quick charge method provided 80% of power to the mobile phone, signifying a four-fold increase and considerably shortened charging time.
Battery capacity of Mobile phone is equivalent to the life of a mobile phone. Although smart phones continue to develop, mobile phone battery technologies have stalled. To solve the problem of short battery life, companies have increased the sizes of mobile phone batteries as well as introduced their own quick charge methods.
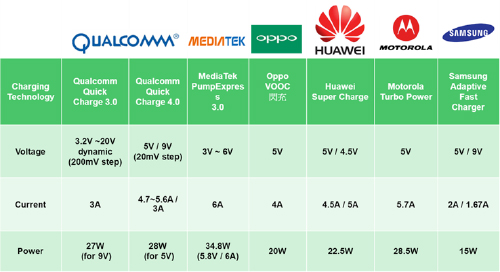
As of today, mainstream quick charge technologies can be divided into high-voltage quick charge and low-voltage quick charge. Concerning high-voltage, low-current quick charge, Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0 to 4.0 and MTK Pump Express/MTK Pump Express plus quick charge are the most popular solutions and enjoy a considerable market share. Regarding low-voltage, high-current quick charge, OPPO VOOC flash charge and Huawei SuperCharge are the most prevalent solutions.
 (Image source / Avnet) (Image source / Avnet)
Of all smart phone-related developments, battery technology remains the only one without a major breakthrough. Accordingly, all companies are employing new alternative methods to improve battery life. All mobile phone users in their daily lives will encounter the situation of lack of mobile phone power, especially those who are heavy users. To such users, they would be satisfied with batteries that can power their mobile phones for one full day. To solve the problem of short battery life while not increasing battery size (so that the external appearances of the mobile phones are not jeopardized), quick charge may be the only viable solution.
Un-unified Charging Accessories for 3C Electronic Products Bring Environmental Issues
When IT products and computer, communication, and consumer electronics products (3C products) are discarded because malfunctions, poor performance, or having gone beyond their service lives, their power supplies and/or charging accessories are often discarded together with them even if they remain functional. Such a practice creates the environmental issue of chargers not being recycled and reused.
To popularize the use of USB power supplies by different electronic devices and reduce power cord installations, a new USB power supply called “USB Power Delivery” (hereafter referred to as “USB PD”) was introduced. In 2012, the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) announced an USB PD power transmission standard called “USB PD,” in which the goals were to deliver 100W of power to all electronic devices via a single USB cable. By shortening the electronic device charging times, it would make mobile electronic device usage much more convenient. USB PD features the advantage of bi-directional transmission, in which electronic devices can transmit data and be charged at the same time. Such a feature saves time, offers convenience, and elevates usage efficiency. In addition, because traditional power cords are no longer needed, USB cords can be unified.
 (Image source / USB-IF) (Image source / USB-IF)
USB PD Applications and Market Conditions
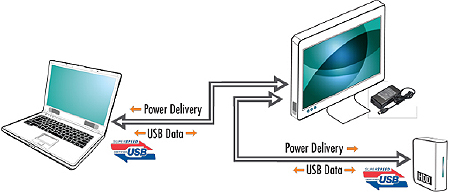
In general, computer towers serve the role of power supply, providing power to connected monitors (however, some monitors may be powered by independent power supplies), laptops, and hard drives. Mobile phones and hard drives are the receiving end of the power supply and draw power from desktop computers or laptops. When the monitor, laptop and tablet all supported USB PD, it showed that they can be used both as the power-supply side and as the power-receiving side. When laptops and tablets are low in battery and no power supply is available, they can be charged by monitors; similarly, when monitors need to be charged, they can be charged using desktop computer towers, laptops, or tablets. When electronic devices such as mobile phones and external hard drives need to receive power, they can be charged by laptops and tablets via the USB Dongle. Likewise, when laptops and tablets are low in battery, they can be charged by mobile phones and hard external drives (data can also be transmitted during this time).
Flexible, bi-directional usage as well as immediate charging can be achieved by installing a USB PD communication IC at the power-supply side and the power-receiving side.
Advantages of the USB PD:
1. By using the single-wire protocol (SWP), single wires can simultaneously transmit power and data.
2. Existing USB standards can be elevated to a power level of 100W.
3. The direction of the power supply is no longer unidirectional. All powered products (e.g., hosts or peripheral devices)
can supply power.
4. By installing the USB PD protocols in two connected electronic devices, the power-supply and power-receiving ends
will be identified, on the basis of which the optimal power supply and reception voltage and current will be determined.
5. USB chargers can use the USB ports of computers to supply power to other electronic devices.
Earlier in this article, the quick charge technologies of various companies were introduced, including the Qualcomm QC, MediaTek PE, OPPO VOOC, Huawei SuperCharge, and USB-IF USB PD. However, because the handshake protocols and technical details between these technologies differ, their quick charge methods are not compatible. In addition, no consensus has been reached concerning which method is the optimal one.
 (Image source / SOGI Net) (Image source / SOGI Net)
Quick charge has already become an essential function for smartphones. However, since various quick charge methods have been presented and selected, suitable quick charge solutions has troubled consumers. Fortunately, these problems will soon disappear as USB-IF updated the PD standards (by adding Programmable Power Supply (PPS) standards) in the spring of 2017. The PPS standards are an important update to the USB PD 3.0 standards, where the objective is to create uniform standards for all current quick charge technologies. Currently, quick charge standards for Qualcomm QC 3.0/4.0, MediaTek PE 2.0/3.0, OPPO VOOC, and Huawei SuperCharge have been successfully incorporated, indicating that the new specifications can support the four quick charge methods. USB-IF and China Telecommunication Technology Labs (of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the People’s Republic of China) have reached an agreement, unifying the international standards in the future.
 (Image source / USB-IF) (Image source / USB-IF)
The battle between the quick charge standards in 2016 has come to an end, and the era of unified standards will take place in 2017. For consumers, they can finally look forward to 2017 being the year when they can start enjoying the convenience of unified chargers.
From idea to design and from prototype to production, Avnet supports customers at each stage of a product’s lifecycle. A comprehensive portfolio of design and supply chain services makes Avnet the go-to guide for innovators who set the pace for technological change. For nearly a century, Avnet has helped its customers and suppliers around the world realize the transformative possibilities of technology. The Avnet Design Services Department has developed a variety of quick charge designs to serve as references to customers when designing circuits. In addition, it provides assistance to its customers whenever needed to minimize the time required for the customers’ products to hit the market.

▲TOP
|
|
|

